Author(s): Kishore.S
Paper Details: Volume 3, Issue 1
Citation: IJLSSS 3(1) 45
Page No: 447 – 461
ABSTRACT
The study examines the impact of social media on social movements in chennai,examining how digital platforms influence public awareness, engagement and the effectiveness of activism. As social media becomes increasingly integral to modern activism, this research aims to understand its role in shaping and mobilizing social movements within the city. By employing a mixed methods approach, including surveys and interviews, the study explores public perceptions of social media’s influence identifies key platforms used, and assess the effectiveness of these digital tools in driving social change.The findings reveal the nuances of social media’s role in chennai’s local context, highlighting differences from other cities and regions.The study contributes to a broader understanding for social activism and offer’s insights.
KEY WORDS
Social,awareness,influence,integral,mobilizing
INTRODUCTION
In the digital age, social media has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping how individuals and communities engage with societal issues and advocate for change. This phenomenon is particularly evident in the context of social movements, where platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and WhatsApp have become pivotal in mobilizing support, raising awareness, and facilitating grassroots activism.Chennai, a bustling metropolis in southern India, is not immune to these global trends. With its diverse population and active civil society, the city has witnessed various social movements seeking to address a range of issues, from environmental concerns to gender equality and political reform. In recent years, social media has played a critical role in these movements, serving both as a tool for dissemination and a space for public discourse.
EVOLUTION OF THE TOPIC
Initial studies focused on traditonal forms of social activism and communication.Social media was emerging as a new tool but not yet a primary platform for mobilization.Social media’s role became more preneutral with the proliferation of platforms such as whatsapp and instagram.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES
Intermediary guidelines and digital media ethics code (2021):The Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code, 2021 is a set of regulations introduced by the Government of India aimed at governing the operations of digital media platforms, including social media companies, news aggregators, and digital news publishers. These guidelines are part of a broader effort to regulate the digital space and ensure accountability and transparency.
CURRENT TRENDS
Localized Activism and Hyperlocal focus: Social movements are increasingly focusing on localized issues specific to communities or cities, leveraging social media to mobilize support for local causes.Cress platform campaigning: Activists are using multiple social media platforms in tandem to reach diverse audiences and enhance their campaigns visibility and impact.
COMPARISON WITH OTHER CITIES
Chennai vs Delhi: Social movements in chennai often leverage localized issues and community- based approaches, with a strong emphasis on regional activism. In delhi,it benefit from a larger media presence and international-scale protests, Delhi’s movements might have broader reach due to national media focus, while chennai movements are localized and community-focused.Chennai vs New tork city: NYC’s social media impact is characterized by its global reach and influence , whereas chennai’s impact is more focused or regional and localized concerns.
OBJECTIVES
- To evaluate the level of public awareness in chennai regarding social movements organized through social media platforms
- To identify which social media platforms are most commonly used and deemed most influential in context of social movements in chennai.
- To determine the extent of public engagement and participation in social movements.
- To investigate the level of trust and credibility that the public assigns to social media as a source of information.
- To explore key factors that motivate individual in chennai to support or participate in social movements.
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
SAHEBRAO(2023)
To examine the role of social media in mobilizing sustaining social movements that lead to social change. Accessibility, individual, engagement, hashtag, activism, online participation and government response,social media effectively mobilizes and sustains social movement driving social change through enhanced accessibility, individual engagement, online activism.
DEANA(2022)
To explore the role of mass media in shaping public understanding mobilizing support for social movements, media types, audience research, resource availability of media,movement and relationship,Mass media effectively amplifies social movements by shaping public perception and mobilizing broader public action, varying impact based on media type resource availability.
OLOVER(2023)
To examine how protest movements adapt to social media logic mobilization efforts communication stratefies.Social media logic timing designs posts resource availability consent sensitivity personalization.Protest movements internalized social media logic tailoring strategies algorithms based available resources they challenges wise sensitive context personalization within the movements.
SUDIP(2024)
To analyze the impact of social media on tension insurgency and identify root causes youth involvement in the movement,social media platforms yath engagement protest authorization, regime,Social media significantly facilitated tension insurgency organizing protests mobilizing youth leading peaceful transmition from authorization regime.
ADEHINA(2023)
To explore social media’s role in EndSARs nonviolent protests movement, social media platforms vice amplification success limitations,social media way keys in mobilizing activists and spreading information during EndSARs but face challenges providing lessons for future protests.
TRIPATHHI(2024)
To explore the pros and cons of using social media for activism and its potential to affect socio political change social media through activism has effectively influenced socio political changes globally despite being a relatively new concept offering valuable insights for activists.
FAFEWARA(2024)
To examine role of social media fake news mobilizing suppressing endSars protests in nigeria,social media fake news manipulatively by both ends advocates Nigerian government catastrophic outcomes consistent HNT-UGT.
HOFFMANN(2024)
To analyze the ase of protest imaginary on social media by movement parties linked to institutional politics,movement parties protest imaginary to amplify grievances of right leaning parties decentralized as they institutionalize varying by county ideology.Gabilian(2023):To examine role of social media LGBTQUA activism in sri lanka particularly northern province, social media significantly amplified LGBTQ empoworemnt sri lanka creating positive societal impacts despite challenges faced by activists.
PADIRECELLI(2024)
To explore role of celebrities in resource mobilization for social movements via digital media using campaign, celebrity involvement social movement in media significantly boosted resource mobilization engagement NO_TAV movement offering insights into impact longevity such endorsements.
AMENTA(2023)
To summarize the findings on media attention US social movements asses impact of modern media dynamics these movements, media attention journalism internet electronic media public sphere conservative movements democracy, despite decline of traditional newspapers national news organizations remain crucial yet current media imbalances favor conservative movements posing a threat to democracy.
ARTZLEE(2022)
To assess the role of corporate run social media in organization social movements focusing Black Lives matter, social media efficiency racial inequality participatory democracy mass protest political independence.Effective social media strategies for social change involve participatory democracy mass protest political independence as seen with Black lives matter.
BARIS COLAN(2013)
To analyze the impact of social media on social movements using specific case studies, social media greatly affects social movements with diverse impacts across different cases.
MILANDI(2016)
The growing impact of new media around the world has been the subject of study by scores of scientists in multidisciplinary fields. Satellite TV and the Internet have been viewed as instruments of social political change connecting communities educating the youth and creating social networks previously unaccounted for like virtual groups.
SUMMEN HARBOW(2012)
The accusations prompted the creation of numerous Facebook pages calling for column registration and for justice reasoning using interviews and a content analysis of facebook comments from the two most effective facebook groups found online movements that move offline.
REV VILGHNET(2012)
Remarkably enough one does not field many of their publications in the journals book volumes scholars intensed in political communication turn to research about social movements is mainly general by sociologists much of this research on movement media is found in sociological journals books.
LAMMONETS(2015)
This entry provides an overview of the ways in which social media digital networks centralized examined in relation to social movement activism,A member of communicative particles that activists display are identified and the ways in which information and communication technology medicated practices are embedded in roles.
DEEN FREELON(2018)
The exercise of power has been an implicit theme in research on the use of social media for politics but few studies have attempted to measure social media power and its consequences directly.
MARIO DIANI(2000)
The potential consequences of CMC expected to effect collective action by improving the effectiveness of communication and facilitating collective identity solitary heterogeneity of social movements undermines genric arguments about their relation to CMC.
MARCO GIGUIANI(2022)
Empirical work was therefore necessary to ascertain the amount of bias in policy process and political systems,his work also controlled for the development of an increasingly namened understanding of the policy process and of the nature of power.
METHODOLOGY
This study has been conducted using the empirical research method. The samples were collected
using a convenient sampling method. A total of 200 samples have been collected for the study.
The sample frame taken here is of public areas in and around Chennai. The dependent variables are age,gender, educational qualification, and the dependent variables are reasons for consumption of junk foods, awareness about health risks, and scale on health. SPSS is the statistical tool used for the study.
DATA ANALYSIS
FIGURE 1
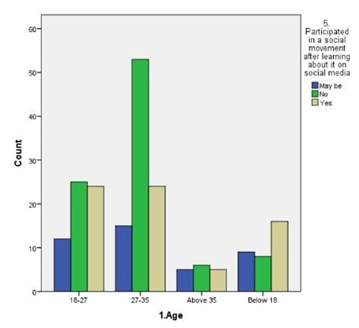
LEGEND: Fig 1 represents the relation between the age and participationof the respondents in social movements by seeing about it in online the majority of age is 27-35.
FIGURE 2
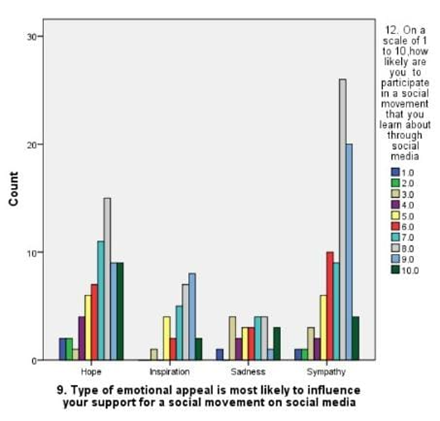
LEGEND: Fig 2 represents the rating of social movements according to the influence reason which supports for participating in it,and graphs clearly says that sympathy is most influenced.
FIGURE 3
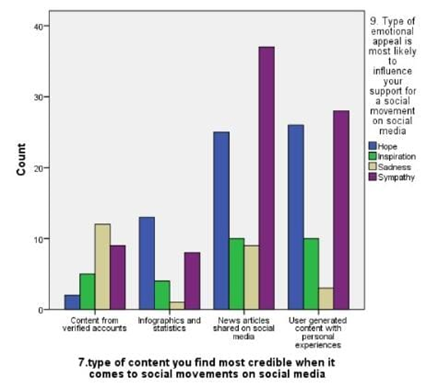
LEGEND: Fig 3 depicts the relation between type of appeal and type of content most credible to trust an online news related to an social movement happening in reality,and it is news articles related on social media.
FIGURE 4
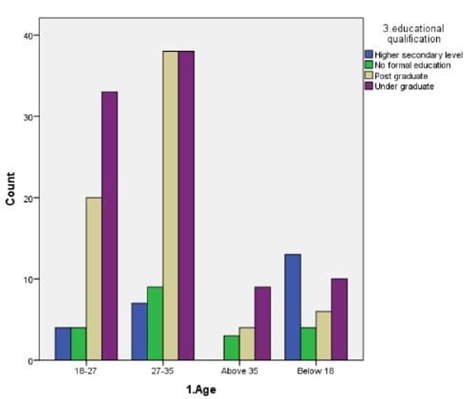
LEGEND: Fig 4 represents the relation between age and educational qualification of respondents and the majority of the respondents were under graduates.
FIGURE 5
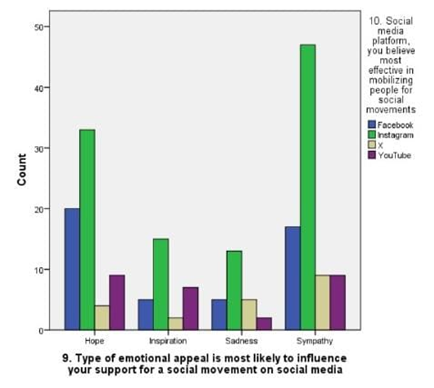
LEGEND: Fig 5 represents the relation between the social media platforms and the content’s appeal to influence your support and the grpah says that sympathy is best reason.
FIGURE 6
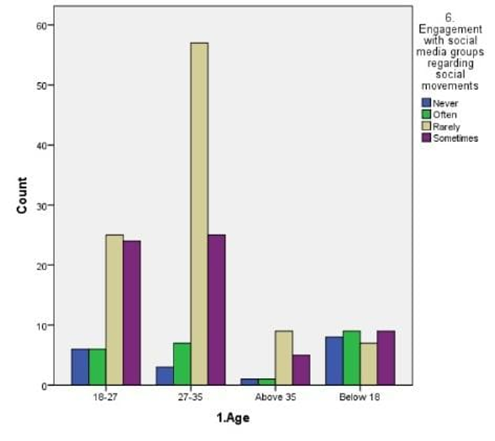
LEGEND: Fig 6 represents the relation between the age and their engagement with social media groups related to social movements and the age is 27-35.
FIGURE 7
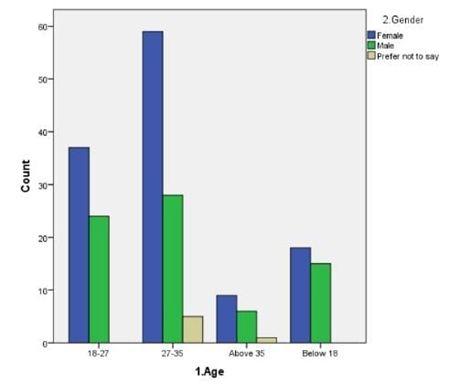
LEGEND: Fig 7 represents the relation between the age and their age and the most of the respondents were female and the age is 27-35.
FIGURE 8
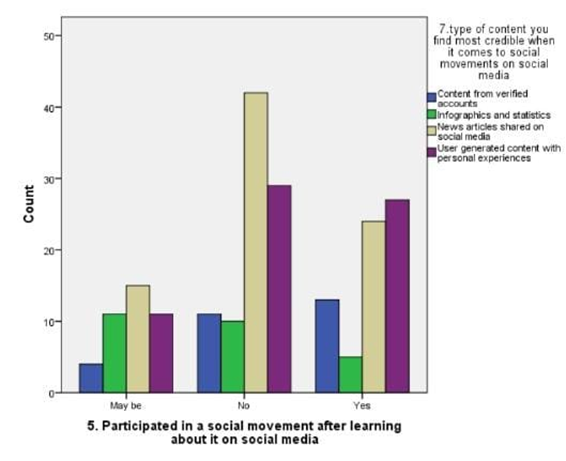
LEGEND: fig 8 shows the relation between the type of content respondent find most credible on social media about social movements and the participation on behalf of learned about it in internet and the highest number of response is NO.
FIGURE 9
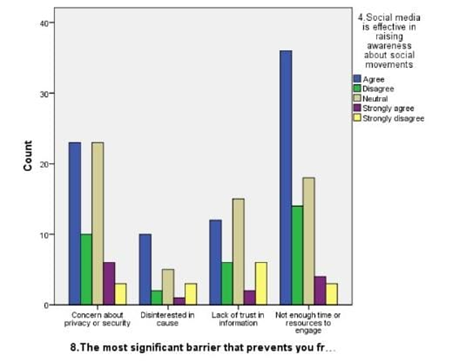
LEGEND: Fig 9 represents the most significant barrier as not enough time and respondents agrees that social media gives awareness about social movements.
FIGURE 10
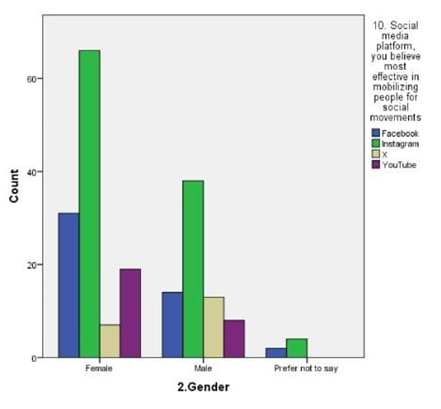
LEGEND: Fig 10 represents the relation between the gender and social media platform they use and its is clear that most of the females and males use instagram.
FIGURE 11
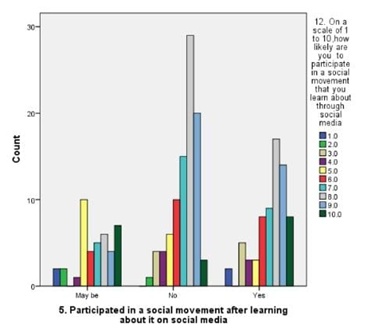
LEGEND: Fig 11 represents the relation between rating and participation on social movements and graph says tha average rating as 8 out of 10 and syas NO to participate.
RESULTS
(Fig 1) represents the relation between the age and participationof the respondents in social movements by seeing about it in online the majority of age is 27-35. (Fig 2) represents the rating of social movements according to the influence reason which supports dor participating in it,and graphs clearly says that sympathy is most influenced.(Fig 3) depicts the relation between type of appeal and type of content most credible to trust an online news related to an social movement happening in reality,and it is news articles related on social media.(Fig 4) represents the relation between age and educational qualification of respondents and the majority of the respondents were under graduates.:( Fig 5) represents the relation between the social media platforms and the content’s appeal to influence your support and the grpah says that sympathy is best reason.( Fig 6 )represents the relation between the age and their engagement with social media groups related to social movements and the age is 27-35.(Fig 7) represents the relation between the age and their age and the most of the respondents were female and the age is 27-35.(fig 8 )shows the relation between the type of content respondent find most credible on social media about social movements and the participation on behalf of learned about it in internet and the highest number of response is NO.(Fig 9) represents the most significant barrier as not enough time and respondents agrees that social media gives awareness about social movements.( Fig 10) represents the relation between the gender and social media platform they use and its is clear that most of the females and males use instagram.(Fig 11) represents the relation between rating and participation on social movements and graph says that average rating as 8 out of 10 and syas NO to participate.
DISCUSSIONS
The findings from the study provide a nuanced understanding of how social media influences participation in social movements, particularly within Chennai. Figure 1 reveals that the majority of participants are in the 27-35 age group, indicating that this demographic is notably active in online social movements. This aligns with the data in Figure 6, which shows significant engagement with social media groups among the same age range. This suggests that younger adults, particularly those who are well-educated but still early in their careers, are driving online activism.Figure 2 and Figure 5 both underscore that sympathy is a major factor influencing participation. This emotional appeal seems to be a key motivator for users, reflecting the importance of emotional resonance in mobilizing support. Despite the high rating of social movements’ effectiveness in Figure 11, there is a notable reluctance to participate, as indicated by the average rating of 8 out of 10 and the response in Figure 9 about time constraints being the primary barrier. This dichotomy between perceived effectiveness and actual engagement points to an underlying issue: while social media effectively raises awareness, practical barriers such as time limitations impede active involvement.Figure 3 highlights that news articles on social media are considered the most credible source of information regarding social movements. This emphasizes the role of quality journalism in shaping public perception and trust, though Figure 8 indicates that many respondents still question the credibility of online content, potentially affecting their participation.Figure 4 and Figure 7 reveal that a majority of respondents are undergraduates and predominantly female, reinforcing the notion that educational background and gender may influence participation patterns. Moreover, Figure 10 shows that Instagram is the most used platform across genders, suggesting its significant role in influencing and mobilizing support for social movements.The statistical analysis further elucidates these findings. Overall, these findings highlight the complex interplay between emotional appeal, content credibility, and practical barriers in shaping social movement participation. The study underscores the need for targeted strategies to address time constraints and improve the credibility of online content to foster more active engagement.
CONCLUSION
This study highlights the significant role of social media in shaping participation in social movements within Chennai, revealing that emotional appeals, particularly sympathy, strongly influence engagement. Despite high ratings for the effectiveness of social media in raising awareness, actual participation is hindered by practical barriers such as time constraints and skepticism about content credibility. The study finds that younger adults, especially those in the 27-35 age range and with undergraduate education, are the most active in online social movements, with Instagram emerging as a key platform for engagement. However, the research is limited by factors such as sample representativeness, reliance on self-reported data, and the rapidly changing nature of social media. These limitations underscore the need for further research to address these gaps and enhance our understanding of how digital platforms impact social activism. Overall, while social media has proven effective in mobilizing support and raising awareness, bridging the gap between perceived effectiveness are that really social media plays huge role in social movements.
REFERENCES
Hiwale,sahelrao.(2024).Impact of social media on social movements.
.Rohlinger,Deana.(2022).Mediaandsocialmovements.10.1002/97804706748171.wbespm128.pub2
.Strenhler-Schroff,Marlene,Oliver(2023).The limits of social media mobilization:How protest movements adapt to social media logic media and communication.11.10.17645/max.v11i3.6635
Ghimise,sudip(2024).The impact of social media in Arab spring: A case of tunisia
Oylongve,Olwanava,Bhabatunde and Omatayo,Adeshina(2023).SOCIAL MEDIA AND NONVIOLENT PROTEST MOVEMENTS:A CONTEMPORARY REVIEW OF THE ENDSARS MOVEMENT volume 7.312
Chopra,Ayushi and Bhatia.varnishka,tripathi,sheel and basena,Sakashi(2024).A STUDY OF SOCIAL MEDIA ACTIVISM IN THE REAL WORLD.49.188-192.
Fakehwara,Bimla(2024).Social media and the weaponizer of fake news; The case of the #EndSARs protest
Hoffmann,matheins and beymar,christian(2024).Images of protest in movement parties social media communication.New media &society. 10.1177/14614448241243532
Gabilian,anutharani,(2023).Qeer activism andempoweremnt on social Media 10.2324/9781003395805-25
Parehebeli,gieupase michale(2024).Rethinking the rsource mobilization theory in social movements digital expression
Amenta, Edwin & Caren,Nweal (2023).The past and future of social movement in the news.10.23943/princeton/9780691232782.003.0008.
Artz,lee(2022).SocialMediaandSocialMovementsprotest.1.248-271.10.1163/2667372x-01030003
Baris coban(2013).Social media and social movements
.Nourenhvile Milandi(2016)Social Media and social change.Digest of middle east stadis 25(1),36-51
.Summer harlow(2012),naver media and society 14 (2),225-243
.Rev,vileghienst, steffan wagufsee(2012).The sage handbook of political communication 387-398
Bart cammarets(2015) social media and activism, Journalism,1027-1034
Deen freelon, Meredith cloak (2018),New media & society 20(3),990-1011
.Mario Diani(2000),Social movement networks virtual and real, Information, communication & society 3(3), 386-401
.Marco giugani(2022),Social movements.The polydegree encyclopedic of interest groups, lobbying and public offices,1213-1221,2022
