Author(s): Aditi Sharma & Rajini Bollera Kushalappa
Paper Details: Volume 3, Issue 3
Citation: IJLSSS 3(3) 48
Page No: 566 – 577
ABSTRACT
In recent years, the financial sector has undergone transformative changes driven by the twin forces of globalization and financial technology (FinTech). Globalization has fostered increased interdependence among world economies, leading to the internationalization of trade, investment, and financial systems—enhancing efficiency, market access, and capital mobility. Simultaneously, FinTech has emerged as a disruptive force, applying technological innovations to financial services and significantly expanding access to finance, especially for underbanked and unbanked populations. These developments have redefined traditional banking models, improved operational efficiency, and introduced customer-centric service paradigms.
This study employs doctrinal analysis combined with qualitative evaluation of global trends to explore the synergistic impact of globalization and FinTech on the contemporary financial landscape. While these shifts present significant opportunities for financial inclusion and economic growth, they also give rise to complex regulatory, cybersecurity, and data privacy challenges. The paper critically examines these dual dynamics, assesses their implications for traditional financial institutions and FinTech enterprises, and offers policy recommendations to help financial systems adapt sustainably and equitably to ongoing innovations.
KEY WORDS
FinTech, Globalisation, Cross border collaborations, International Monetary Fund, Payment System, Financial landscape, Blockchain Technology
INTRODUCTION
Today, the financial industry stands as one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving sectors of the global economy, undergoing unprecedented transformation driven by the dual forces of globalization and technological innovation. The dissolution of traditional trade barriers, liberalization of capital markets, and the seamless flow of information and investments across borders have created a deeply interconnected financial landscape—one where decisions made in one region can have immediate ripple effects worldwide. At the same time, financial technology, or FinTech, has revolutionized the delivery and consumption of financial services, introducing tools such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, digital wallets, and algorithmic lending that are redefining traditional models of banking, credit, and payment systems. While globalization has enabled broader access to international markets and investment opportunities, FinTech has accelerated financial inclusion and operational efficiency, particularly for underbanked and remote populations. However, the convergence of these two forces is not without challenges, including cybersecurity threats, regulatory fragmentation, and ethical concerns surrounding data privacy and algorithmic governance.
Despite the growing importance of this intersection, much of the existing literature has examined globalization and FinTech in isolation, leaving a significant gap in understanding how their integration is jointly reshaping the global financial ecosystem. This research seeks to address that gap by exploring how globalization facilitates the diffusion and evolution of FinTech across borders, what implications these innovations hold for legacy financial institutions, and how stakeholders—from policymakers to private enterprises—can respond effectively to maximize opportunities while mitigating risks. Through doctrinal analysis and qualitative review of recent developments, the study aims to uncover the opportunities, disruptions, and regulatory complexities that define this new era of finance. In doing so, it proposes a set of forward-looking recommendations to build a resilient, inclusive, and ethically governed financial system that is responsive to the needs of an increasingly digital and borderless world.
GLOBALIZATION’S ROLE IN RESHAPING INTERNATIONAL BANKING AND INVESTMENT PRACTICES
MEANING OF GLOBALISATION
The term Globalisation has been used to denote “liberalization, Westernization, homogenization, economic growth and decline, equality and inequality, and so on”.[1] Moreover, WHO has also described the term globalisation as deepening interdependence and interconnection between people and nations which can be described by two processes that are flow of goods, services, finance and ideas across national borders[2] second is the process of creation and strengthening of national and international structures and policies that support and enable such flows.[3]
FINANCIAL GLOBALISATION
If we want to define globalization in the context of financial sector, then we can say that “Financial globalization” is the interconnection of the global financial markets that are built through cross border financial operations that have different impacts on the emerging and developing economy.[4] It can be a driving force towards development, strengthening the financial sector, and promoting sustainable economic growth and innovation.[5] This integration enhances synergy and reduces risks while at the same time enhancing economic growth and stability among countries. Globalization is an important factor linking the functioning of the financial market and financial security, which affects the national security and stability. In the globalised era financial institutions play a crucial role by providing the necessary infrastructure to support and increase cross-border transactions and investments.[6]
IMPACT OF GLOBALISATION ON FINANCIAL INDUSTRY
In today’s modern world, globalization has emerged as a major force bringing significant changes in various industries. The financial sector, being one of the key pillars of the modern economy is also impacted by globalisation. As market becomes more interdependent and integrated there is need to thoroughly examine the impact of globalisation. The influence of globalisation on financial sector can be highlighted through the following-
1. Increased interconnectivity: This has been due to globalization that has promoted the interconnection and dependence of different financial markets and institutions in the world. This development will in turn enhance access to capital for investors, businessman and individuals and also ease the process of cross border transactions.[7]
2. Increased cross border financial flow: There is nothing to deny by saying that cross border transactions in exchange of goods and services have increased due to globalisation. Therefore, the need for financial services for international transactions has grown and in turn, to meet the needs of the market, financial institutions have established themselves internationally and also introduced some new products and services to meet the needs of customers all over the world and as a solution to this purpose, financial integration has been highlighted as a comparative advantage, particularly for industries whose major focus is on external information. However, the success of financial integration is also affected by legal institutions.[8]
3. Better risk diversification: By embracing globalisation, investors can reduce their risks since they can invest in various markets hence slow economic growth will not greatly affect their portfolio.[9] Diversifying investments across different markets will help in balancing risk and minimizes reliance on a single economy. Various studies have demonstrated that diversified investing in stocks, particularly in countries with low domestic returns, offers better long-term gains for investors.
In our opinion Globalization has without doubt impacted the financial sector through the promotion of cross-border financial flow which enhances interconnectivity, enhances the diversification of risks, as well as harmonization of regulations and driving of financial innovation. These changes have brought about many openings to people and companies to access global markets. But it also poses challenges like compliance to laws and other risks that comes with it. In general, the globalization process affected the financial sector and its future dramatically and will keep on doing that.
FINTECH: AN OVERVIEW
Fintech also known as Financial Technology is “a cross-disciplinary subject that combines Finance, Technology Management and Innovation Management.”[10] This industry utilizes innovative use of technology in the financial sector such as big data analytics, blockchain technology and Artificial Intelligence With the help of latest innovations like big data, blockchain and AI it aims to improve and simplify financial services. Fintech is responsible for the introduction of new financial products and services, and also payment models like digital payments such as Paytm, robo-advisors, online lending platforms and also digital money such as cryptocurrency and Central bank digital currency. The primary objective of these financial technology is to facilitate efficient access to financial services, reduce costs, improve user experience, and promote global financial inclusion.
FINTECH INNOVATIONS
The use of FinTech products and solutions has greatly impacted the financial sector in the improvement of convenience, speed and access. Major innovations include:
- Mobile Banking: Mobile banking and payment apps revolutionize access to financial accounts and transactions, eliminating the need for bank visits and reducing transaction times.
- Blockchain Technology: This decentralized ledger technology ensures transparent and secure financial transactions, potentially disrupting traditional banking with applications like cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, and asset tokenization.[11]
- Robo-Advisors: Automated platforms using AI and machine learning provide personalized investment advice, democratizing investment management with affordable solutions for all income levels.[12]
- P2P Lending: Peer-to-peer lending platforms connect borrowers directly with investors, offering faster loan processes and competitive interest rates.
- Financial Inclusion: FinTech solutions enhance financial inclusion for unbanked and underbanked populations through mobile money, digital wallets, microloans, and neo-banks.[13]
These innovations compel traditional institutions to adapt, fostering a more inclusive, efficient, and strengthened global economy.
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN GLOBALIZATION AND FINTECH
Globalization and FinTech are continuously shaping the modern financial system. Due to globalisation, there is no restrictions on moving across nations and people can travel anywhere. According to a survey in year 1990 there were just 435 million tourist arrivals across countries but in 2018 this number rose to 1.4 billion which depicts how fast we are growing. The amount of foreign currency people is using to make payments for vacations, receiving money from overseas has increased need for a seamless global banking was provided by FinTech. The changing demands of people and businesses in modern globalised world can be met by innovations in payment solutions. During the globalization new tendencies in the development of financial market appeared that provided it with an innovative character and the development of Fintech’s brought digitalization in financial services.[14] The significant rise of these factors has crucial impact on the landscape of modern financial system resulting in growth of cross border transactions, flow of goods and services and also led to good relations among the nations. These advancements enable faster and secured transactions, improved risk management, and enhanced customer experiences.[15] For example, Fintech enterprises like stripe has developed solutions that enables businesses to accept payments from the customers worldwide.
Globalisation has connected businesses and consumers and there is a need for better and cheaper financial services and this is where FinTech comes in with new products and services which are cheaper, faster and easily accessible than the traditional financial services. The FinTech companies are not strictly regulated because it is still in evolving stage and this enables it to provide obstacles for the traditional banking system, because the services provided by these technologies attract huge chunk of consumers increasing competition for these banks which forces them to adapt new technologies or collaborate with these Fintech institutions so that both can provide best of their services, benefits of accessibility and efficiency. However, benefits come with certain challenges like cyber security risk, privacy risk, technical and technological challenges etc which creates a need of a regulator to impose strict regulations on these institutions and create a balance of innovation with proper safeguard.[16]
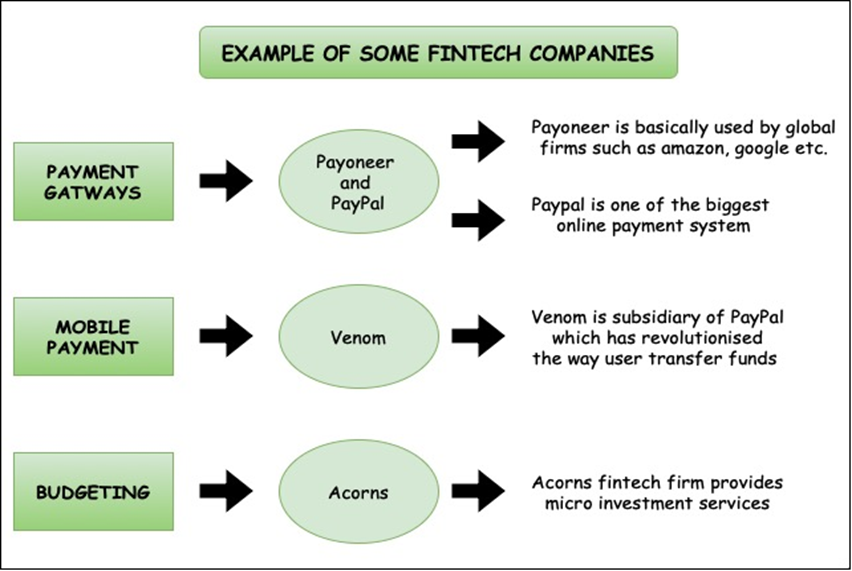
Figure : Top FinTech Companies
CHALLENGES FACED BY FINTECH
Globalization has brought several issues to the FinTech industry, mainly focusing on analysing the global financial markets and local regulations. Challenges faced by Fintech are explained as follows-
- Lack of Proper Regulation: A major issue with FinTech is that the regulatory structure is not well developed. Every country has its own financial laws which cause problems for FinTech companies that want to expand their operations internationally. This fragmentation leads to higher costs and complexities in compliance and it becomes a major issue especially for new entrant firms with limited capital as compared to large firms. This is why there must be a single and unambiguous set of rules that would regulate the work of such companies.
- Cybersecurity Issues: As financial services become more interconnected and digitized, the risks of cyber threats increase. These companies store a huge volume of personal data about their customers making protection of sensitive data crucial for fintech firms, as cybercriminals often target this information. Over the past few years, Internet Crime Complaint Centre of the US recorded 1.42 million internet crimes worldwide, which caused a total loss of USD 5.52 billion. Also, the largest losses were caused in the year 2017 by business email compromised over USD 675 million, confidence fraud and cyber scams were around USD 211 million and non-payment or non-delivery of financial goods scams were recorded more than USD 141 million.[17] In order to combat these risks, there is need to implement security measures and adhere to data privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)[18].
- Diverse Customer Needs: Globalization makes FinTech firms to provide for a wide market that includes different needs and demands of the customers. Product or services which are popular in one market may not be well accepted in another market due to cultural, social or economic factors. Therefore, FinTech firms need to dedicate resources to research and development in order to better adapt to the various markets.
CROSS BORDER FINANCIAL COLLABORATIONS AND GLOBALISATION
Cross border financial collaboration means the financial transaction between two or more nations. These transactions may include exchange of goods and services, increased number of foreign direct investments etc.[19] These collaborations have become more significant in recent year as there is increased economic integration worldwide due to globalisation. There are number of ways in which cross border collaborations have been impacted such as-
First of all, it has improved and streamlined the efficiency of financial institutions which operates around different borders and this was made possible only due to advancements like internet and mobile banking, these institutions can now serve customers anywhere in the world.
Secondly globalisation has reduced the cost of transportation, trade barriers and has advanced communication technologies thus making it easier for the financial institutions to invest in foreign markets and extend their services to foreign clients. For instance, the trade of goods as a proportion of the world’s gross domestic product increased from 21% in 1987 to 30 % in 1997.[20]
Thirdly, financial institutions have been compelled to innovate and provide more productive offerings because of increased competition due to globalised economy. This presents consumers and companies with more options and lower costs.
THE POTENTIAL IMPACT OF RINSING FINTECH CHALLENGE ON THE GLOBAL BANKING SYSTEM
The phenomenon of FinTech is still in its growth phase and it presents significant threats to the conventional banking organizations. One is the intensified competition from the emerging FinTech firms arising from shifting customer perceptions, availability, and ease of technology, and convenience. This competition is most apparent in the following segments such as payments, simple savings, and consumer credit. Also, FinTech innovations cause disintermediation and affect the commercial banks’ liquidity and profitability as they are no longer needed.[21]
Another major concern for banks is data security and privacy which are other major concerns that add to the overall cost by requiring banks to spend a lot on security and to adhere to regulations such as GDPR. In addition, new and constantly changing laws and regulations that are specific to FinTech companies impose new compliance challenges on the existing banks.
Nevertheless, all these challenges can be turned into strengths by finding strategic partners or merging with other firms. Banks, therefore, need to consider engaging with FinTech firms since partnerships help to provide better products and services, enhance organizational processes, and access new customers. Some examples include, the partnership between the Santander Bank and Funding Circle and Citigroup starting the Citi FinTech unit.
FUTURE OUTLOOK OF FINTECH
Fintech is a widely growing term which is used to describe technological innovation in the financial industry. It is possible that leading technology companies, traditional banks, and even market regulators may work together more and more, fostering innovation. The use of Fintech is continuously increasing as according to reports year 2015 to 2019 has seen a drastic increase in the adoption of Fintech from 16% to 64% and also the Covid pandemic has pushed it further with the value of Fintech market reaching USD 730.718 billion in 2020.[22]Thus we can say that the technological advancement in financial sector has very much potential to become the Future of financial sector. Also, there are some recent developments in Fintech sector which shows the future potential such as –
Recent FinTech developments are reshaping the financial landscape:
- Digital Currency: The fiat money is replaced by digital tokens of equal face value as a medium of exchange. Though cryptocurrencies are uncontrolled and distributed, the Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) that are backed by the central government can bring transformation in the financial structure, and can be less costly and time-consuming and more convenient as compared to the traditional methods.
- Financial Inclusion: As it is seen, it has facilitated the delivery of financial services to the needed population globally by making it cheaper. Electronic payments, mobile money, UPI and other online banking facilities extend the financial sector to the unbanked and underbanked especially in the developing world.
- Green Finance: Such inventions as cryptocurrencies, CBDCs, and digital wallets help to minimize the use of paper money, which in turn saves money and contributes to environmental conservation. For instance, the Reserve Bank of India said that it spends an estimated Rs 500 crore on paper money each year, which could be used for developmental purpose.
Hence considering the above examples of how fintech in globalisation era is shaping the future of finance by making the services more accessible, innovative and affordable all over worldwide. Thus, we can say that the fintech has a bright future in the upcoming period although several challenges will come like cybersecurity issues, technical errors etc but they can be resolved.
CONCLUSION
Thus, it can be stated that globalization and FinTech innovations have a tremendous impact on the development of the financial sector, increasing its effectiveness, availability, and international transactions. These changes are capable of leading to an improvement in the economy and the provision of financial services, which on the other hand come with some risks such as privacy, security, and the legal issues. International partnerships increase competition and create opportunities to expand into new markets and advance the FinTech industry. The incumbent financial institutions have to reinvent themselves and partner with the FinTech firms in order to stay relevant. The positive change in the global financial system will be further accelerated by adopting digital currency, artificial intelligence and green finance.
To promote sustainable growth in the future, traditional banks should engage FinTech firms, governments should support cross-border collaboration and guarantee the creation of sound regulatory framework. Customers’ information should be safeguarded and one way of doing this is to avoid cases of unauthorized access to the information. From the three aspects of regulation, technology, and customer satisfaction, financial institutions can be successful in the world and the development of FinTech.
REFERENCES
- Arner DW, Barberis JN and Buckley RP, ‘FinTech and RegTech: Impact on Regulators and Banks’ (2017) 1 Journal of Banking Regulation 1.
- Zetzsche DA, Buckley RP, Arner DW and Barberis JN, ‘From FinTech to TechFin: The Regulatory Challenges of Data-Driven Finance’ (2020) 14 New York University Journal of Law and Business 393.
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, Sound Practices: Implications of FinTech Developments for Banks and Bank Supervisors (Bank for International Settlements, February 2018) https://www.bis.org/bcbs/publ/d431.htm accessed 21 June 2025.
- Financial Stability Board, FinTech and Market Structure in Financial Services: Market Developments and Potential Financial Stability Implications (14 February 2019) https://www.fsb.org/wp-content/uploads/P140219.pdf accessed 21 June 2025.
- Gabor D and Brooks S, ‘The Digital Revolution in Financial Inclusion: International Development in the FinTech Era’ (2017) 28 New Political Economy 1.
- Buckley RP, Arner DW and Zetzsche DA, ‘FinTech for Financial Inclusion: A Framework for Digital Financial Transformation’ (2019) 20 Singapore Journal of Legal Studies 1.
- European Commission, FinTech Action Plan: For a More Competitive and Innovative European Financial Sector (8 March 2018) COM(2018) 109 final.
- Reserve Bank of India, Report of the Working Group on FinTech and Digital Banking (November 2017) https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PublicationReport/Pdfs/WG_FINTEDDBD1A20FBE1B44F3EBA5CA0E8B6AD4A5.PDF accessed 21 June 2025.
- World Bank Group, The Global Findex Database 2021: Financial Inclusion, Digital Payments, and Resilience in the Age of COVID-19 (2022) https://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/globalfindex accessed 21 June 2025.
- European Parliament, Digital Finance: Emerging Risks in Crypto-assets – Regulatory and Supervisory Challenges in the Area of Financial Services, Institutions and Markets (April 2021) PE 662.928.
[1] Danny Cassimon, Peter-Jan Engelen and Hanne Van Cappellen, ‘Globalization’ [2018] Springer eBooks 1 <https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007/978-1-4614-7883-6_194-1> accessed 28 August 2024
[2] Abdi O, Qasaye M and Mohamed OA, “The Impact of Globalisation on International Relations” (International Journal of Science and Research, March 19, 2024) <https://www.researchgate.net/publication/379053413_The_Impact_of_Globalisation_on_International_Relations> accessed June 21, 2025
[3] ‘What Is Globalization? Examples, Definition, Benefits and Effects’ (youmatter-dev25 March 2024) <https://youmatter.world/en/definitions/definitions-globalization-definition-benefits-effects-examples/> accessed 31 August 2024.
[4] Sanjay Bulaki Borad and Sanjay Bulaki Borad, ‘Financial Globalization – Meaning, Benefits, and Criticisms’ (eFinanceManagement 17 January 2022) <https://efinancemanagement.com/financial-management/financial-globalization> accessed 28 August 2024
[5] Strike Mbulawa, ‘Rethinking Financial Globalization’ (2023) IntechOpen eBooks <https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/84612> accessed 28 August 2024
[6] Following the Money (1995) <https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/2134/chapter/3> accessed 28 August 2024
[7] Ibid.
[8] Jung Hur, Manoj Raj and Yohanes E Riyanto, ‘Finance and Trade: A Cross-Country Empirical Analysis on the Impact of Financial Development and Asset Tangibility on International Trade’ (2006) 34 World Development 1728 <https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0305750X06001148> accessed 28 August 2024
[9] ‘How Globalization Impacts International Investments and Economies’ (Investopedia2024) <https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/022615/what-effect-has-globalization-had-international-investments.asp> accessed 31 August 2024.
[10] Kelvin Leong, ‘FinTech (Financial Technology): What Is It and How to Use Technologies to Create Business Value in Fintech Way?’ (2018) 9 International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology 74 <http://www.ijimt.org/vol9/791-M775.pdf> accessed on 28 August 2024
[11] Imane Adel, ‘Council Post: How Blockchain Is Transforming the Entire Financial Services Industry’ Forbes (12 August 2024) <https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2023/06/07/how-blockchain-is-transforming-the-entire-financial-services-industry/#:~:text=As%20a%20secure%2C%20decentralized%20and%20transparent%20ledger%20system%2C,to%20improved%20efficiency%2C%20reduced%20costs%20and%20enhanced%20security.> accessed on 28 August 2024
[12] ‘Personalized Robo-Advising: Enhancing Investment through Client Interaction | Management Science’ (Management Science2024) <https://pubsonline.informs.org/doi/10.1287/mnsc.2021.4014> accessed on 28 August 2024
[13] ‘The FinTech Route to Greater Financial Inclusion in India’ <https://www.pwc.in/assets/pdfs/consulting/financial-services/fintech/point-of-view/the-fintech-route-to-greater-financial-inclusion-in-india.pdf>. accessed on 28 August 2024
[14] Elena Travkina and Molokanov Alexander, ‘Modern Types of Financial Innovations in the Conditions of Digitalization of the Global Banking System’ (2019) 85 Advances in Economics, Business and Management Research 18 <https://www.atlantis-press.com/proceedings/icoeme-19/125910759> accessed 29 August 2024
[15] Fidelis Anake Atseye and others, ‘Globalisation and Implications for the Marketing of Financial Services: A Theoretical Review’ (ResearchGate2022) <https://www.researchgate.net/publication/379693436_Globalisation_and_Implications_for_the_Marketing_of_Financial_Services_A_Theoretical_Review> accessed 29 August 2024
[16] ‘Securing the Future: Enhancing Cybersecurity in 2024 and Beyond’ (ISACA2024) <https://www.isaca.org/resources/news-and-trends/isaca-now-blog/2024/securing-the-future-enhancing-cybersecurity-in-2024-and-beyond> accessed 29 August 2024
[17] Fahri Murshudli & Boris Loguinov, ‘Digitalization Challenges to Global Banking Industry’ (2019) 37th International Scientific Conference on Economic and Social Development -Socio Economic Problems of Sustainable Development 787,793 < https://www.proquest.com/docview/2188521266?fromopenview=true&pq-origsite=gscholar&parentSessionId=nsaCrOZUOVGVmMO9mNRFmFx3kJWWmVDIfNZJe0DGy44%3D> accessed 29 August 2024
[18] The term “GDPR” is a comprehensive data privacy regulation in the European Union that aims to protect individuals’ personal information and give them greater control over their data, requiring businesses to be transparent and accountable in their data processing activities.
[19] The term “Foreign direct investment (FDI)” refers to an investment made by an individual or a company The term FDI stands for the foreign direct investment and it can be defined as the investment made by an entity in one country in the business interests or assets located in another country. Usually it entails setting up operations, purchasing stakes in local firms or investing in equity of foreign businesses with a view of catalysing their growth and increasing their market share.
[20] Supra Note 11
[21] Inna Romanova and Marina Kudinska, ‘Banking and Fintech: A Challenge or Opportunity?’ (2016) 98(1) Emerald Group Publishing Limited 21,28 <https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/S1569-375920160000098002/full/html> accessed 29 August 2024
[22] Thomas Philippon, ‘NBER working paper series the fintech opportunity’ (2016) <https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w22476/w22476.pdf>.accessed 29 August 2024
